3D printers use one of the following methods to build an object layer by layer:
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY #1: FUSED DEPOSITION MODELING (FDM)
This is the most common technology used in desktop 3D printers. Thermoplastic material is heated and extruded through a nozzle. The nozzle deposits the molten material layer by layer onto a build platform. Each layer sticks to the one beneath it.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY #2: STEREOLITHOGRAPHY (SLA)
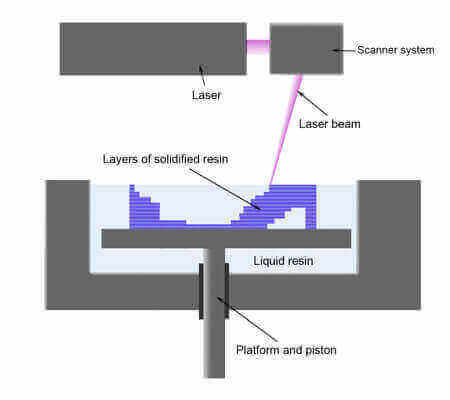
The build platform is lowered into a bath filled with a special liquid photopolymer resin. The resin is light-sensitive and becomes solid when exposed to a laser beam. Each cross section of the 3D model is traced onto the layer of cured resin that came before it. This is repeated layer by layer until the 3D object is completed.
In FDM the object is built from the bottom up, in SLA it’s the other way round.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY #3: SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING (SLS)
This process involves a laser beam fusing powdered material together. The first layer of powdered material is evenly rolled onto the build platform after which the layer of the 3D model is fused together by a laser. Next, the build platform is lowered by the width of one layer, and the next layer of powder is rolled into position. This process is repeated until the 3D object is finished. Since the object is surrounded by (unused) material throughout the duration of the build, support structures are not necessary like they sometimes are with the FDM process.
Many different materials can be used with this technology from plastics to metals.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY #4: SELECTIVE LASER MELTING (SLM)
SLS works on the same principal as the SLS process but uses a higher intensity laser and only metal powder. In this process, the tiny metal particles are actually melted together to form a solid piece of metal as if machined from one solid block.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY #5: BINDER JETTING
Binder Jetting also uses a powder bed as its source of material. But instead of a laser, the powder, e.g. metal, is first “glued” together using an adhesive binder after which the object is heat-treated in a kiln to set or fuse the material.
To get colored prints, you can add pigments to the binding materials.